| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 5.0 |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Quantified |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2005-11-16 15:48:42 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2025-05-29 18:10:03 UTC |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0000148 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | |
|---|
| Metabolite Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Glutamic acid |
|---|
| Description | Glutamic acid (Glu), also known as L-glutamic acid or as glutamate, the name of its anion, is an alpha-amino acid. These are amino acids in which the amino group is attached to the carbon atom immediately adjacent to the carboxylate group (alpha carbon). Amino acids are organic compounds that contain amino (-NH2) and carboxyl (-COOH) functional groups, along with a side chain (R group) specific to each amino acid. L-glutamic acid is one of 20 proteinogenic amino acids, i.e., the amino acids used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Glutamic acid is found in all organisms ranging from bacteria to plants to animals. It is classified as an acidic, charged (at physiological pH), aliphatic amino acid. In humans it is a non-essential amino acid and can be synthesized via alanine or aspartic acid via alpha-ketoglutarate and the action of various transaminases. Glutamate also plays an important role in the body's disposal of excess or waste nitrogen. Glutamate undergoes deamination, an oxidative reaction catalysed by glutamate dehydrogenase leading to alpha-ketoglutarate. In many respects glutamate is a key molecule in cellular metabolism. Glutamate is the most abundant fast excitatory neurotransmitter in the mammalian nervous system. At chemical synapses, glutamate is stored in vesicles. Nerve impulses trigger release of glutamate from the pre-synaptic cell. In the opposing post-synaptic cell, glutamate receptors, such as the NMDA receptor, bind glutamate and are activated. Because of its role in synaptic plasticity, it is believed that glutamic acid is involved in cognitive functions like learning and memory in the brain. Glutamate transporters are found in neuronal and glial membranes. They rapidly remove glutamate from the extracellular space. In brain injury or disease, they can work in reverse and excess glutamate can accumulate outside cells. This process causes calcium ions to enter cells via NMDA receptor channels, leading to neuronal damage and eventual cell death, and is called excitotoxicity. The mechanisms of cell death include: Damage to mitochondria from excessively high intracellular Ca2+. Glu/Ca2+-mediated promotion of transcription factors for pro-apoptotic genes, or downregulation of transcription factors for anti-apoptotic genes. Excitotoxicity due to glutamate occurs as part of the ischemic cascade and is associated with stroke and diseases like amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, lathyrism, and Alzheimer's disease. Glutamic acid has been implicated in epileptic seizures. Microinjection of glutamic acid into neurons produces spontaneous depolarization around one second apart, and this firing pattern is similar to what is known as paroxysmal depolarizing shift in epileptic attacks. This change in the resting membrane potential at seizure foci could cause spontaneous opening of voltage activated calcium channels, leading to glutamic acid release and further depolarization (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glutamic_acid). Glutamate was discovered in 1866 when it was extracted from wheat gluten (from where it got its name. Glutamate has an important role as a food additive and food flavoring agent. In 1908, Japanese researcher Kikunae Ikeda identified brown crystals left behind after the evaporation of a large amount of kombu broth (a Japanese soup) as glutamic acid. These crystals, when tasted, reproduced a salty, savory flavor detected in many foods, most especially in seaweed. Professor Ikeda termed this flavor umami. He then patented a method of mass-producing a crystalline salt of glutamic acid, monosodium glutamate. |
|---|
| Structure | InChI=1S/C5H9NO4/c6-3(5(9)10)1-2-4(7)8/h3H,1-2,6H2,(H,7,8)(H,9,10)/t3-/m0/s1 |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| (S)-2-Aminopentanedioic acid | ChEBI | | (S)-Glutamic acid | ChEBI | | Acide glutamique | ChEBI | | Acido glutamico | ChEBI | | Acidum glutamicum | ChEBI | | E | ChEBI | | Glu | ChEBI | | Glutamate | ChEBI | | GLUTAMIC ACID | ChEBI | | L-Glu | ChEBI | | L-Glutaminic acid | ChEBI | | L-Glutaminsaeure | ChEBI | | (S)-2-Aminopentanedioate | Generator | | (S)-Glutamate | Generator | | L-Glutaminate | Generator | | L-Glutamate | Generator | | D-Glutamate | MeSH | | L Glutamate | MeSH | | L Glutamic acid | MeSH | | Aluminum L glutamate | MeSH | | Aluminum L-glutamate | MeSH | | Potassium glutamate | MeSH | | D Glutamate | MeSH | | Glutamate, potassium | MeSH | | Glutamic acid, (D)-isomer | MeSH | | L-Glutamate, aluminum | MeSH | | (2S)-2-Aminopentanedioate | HMDB | | (2S)-2-Aminopentanedioic acid | HMDB | | (S)-(+)-Glutamate | HMDB | | (S)-(+)-Glutamic acid | HMDB | | 1-amino-Propane-1,3-dicarboxylate | HMDB | | 1-amino-Propane-1,3-dicarboxylic acid | HMDB | | 1-Aminopropane-1,3-dicarboxylate | HMDB | | 1-Aminopropane-1,3-dicarboxylic acid | HMDB | | 2-Aminoglutarate | HMDB | | 2-Aminoglutaric acid | HMDB | | 2-Aminopentanedioate | HMDB | | 2-Aminopentanedioic acid | HMDB | | a-Aminoglutarate | HMDB | | a-Aminoglutaric acid | HMDB | | a-Glutamate | HMDB | | a-Glutamic acid | HMDB | | Aciglut | HMDB | | alpha-Aminoglutarate | HMDB | | alpha-Aminoglutaric acid | HMDB | | alpha-Glutamate | HMDB | | alpha-Glutamic acid | HMDB | | Aminoglutarate | HMDB | | Aminoglutaric acid | HMDB | | Glt | HMDB | | Glusate | HMDB | | Glut | HMDB | | Glutacid | HMDB | | Glutamicol | HMDB | | Glutamidex | HMDB | | Glutaminate | HMDB | | Glutaminic acid | HMDB | | Glutaminol | HMDB | | Glutaton | HMDB | | L-(+)-Glutamate | HMDB | | L-(+)-Glutamic acid | HMDB | | L-a-Aminoglutarate | HMDB | | L-a-Aminoglutaric acid | HMDB | | L-alpha-Aminoglutarate | HMDB | | L-alpha-Aminoglutaric acid | HMDB | | 2-Acetamido-2-deoxy-D-glucose | HMDB | | D-GlcNAc | HMDB | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine | HMDB | | N-Acetylchitosamine | HMDB | | N Acetyl D glucosamine | HMDB | | 2 Acetamido 2 deoxy D glucose | HMDB | | 2 Acetamido 2 deoxyglucose | HMDB | | 2-Acetamido-2-deoxyglucose | HMDB | | Acetylglucosamine | HMDB | | 3alpha,7alpha,12alpha-Trihydroxy-5beta-cholan-24-oylglycine | HMDB | | N-[(3alpha,5beta,7alpha,12alpha)-3,7,12-Trihydroxy-24-oxocholan-24-yl]glycine | HMDB | | N-Choloylglycine | HMDB | | 3a,7a,12a-Trihydroxy-5b-cholan-24-oylglycine | HMDB | | 3Α,7α,12α-trihydroxy-5β-cholan-24-oylglycine | HMDB | | N-[(3a,5b,7a,12a)-3,7,12-Trihydroxy-24-oxocholan-24-yl]glycine | HMDB | | N-[(3Α,5β,7α,12α)-3,7,12-trihydroxy-24-oxocholan-24-yl]glycine | HMDB | | Glycocholate | HMDB | | Glycine cholate | HMDB | | Glycocholic acid, sodium salt | HMDB | | Cholylglycine | HMDB | | Glycocholate sodium | HMDB | | 3alpha,7alpha,12alpha-Trihydroxy-5beta-cholanic acid-24-glycine | HMDB | | 3alpha,7alpha,12alpha-Trihydroxy-N-(carboxymethyl)-5beta-cholan-24-amide | HMDB | | 3Α,7α,12α-trihydroxy-5β-cholanic acid-24-glycine | HMDB | | 3Α,7α,12α-trihydroxy-N-(carboxymethyl)-5β-cholan-24-amide | HMDB | | Glycoreductodehydrocholic acid | HMDB | | Glycylcholate | HMDB | | Glycylcholic acid | HMDB | | N-(Carboxymethyl)-3alpha,7alpha,12alpha-trihydroxy-5beta-cholan-24-amide | HMDB | | N-(Carboxymethyl)-3α,7α,12α-trihydroxy-5β-cholan-24-amide | HMDB | | N-Choloyl-glycine | HMDB | | 3-Hydroxy-1,3,5(10)-estratrien-17-one | HMDB | | Follicular hormone | HMDB | | Folliculin | HMDB | | Oestrone | HMDB | | (+)-Estrone | HMDB | | 1,3,5(10)-Estratrien-3-ol-17-one | HMDB | | 3-Hydroxy-17-keto-estra-1,3,5-triene | HMDB | | 3-Hydroxyestra-1,3,5(10)-trien-17-one | HMDB | | 3-Hydroxyestra-1,3,5(10)-triene-17-one | HMDB | | 3-Hydroxyoestra-1,3,5(10)-trien-17-one | HMDB | | D1,3,5(10)-Estratrien-3-ol-17-one | HMDB | | Estrone, (+-)-isomer | HMDB | | Hyrex brand OF estrone | HMDB | | Estrone, (9 beta)-isomer | HMDB | | Estrovarin | HMDB | | Kestrone | HMDB | | Wehgen | HMDB | | Estrone, (8 alpha)-isomer | HMDB | | Hauck brand OF estrone | HMDB | | Unigen | HMDB | | Vortech brand OF estrone | HMDB | | alpha,beta-Hydroxypropionic acid | HMDB | | D-GroA | HMDB | | R-Glyceric acid | HMDB | | Glycerate | HMDB | | (R)-Glycerate | HMDB | | a,b-Hydroxypropionate | HMDB | | a,b-Hydroxypropionic acid | HMDB | | alpha,beta-Hydroxypropionate | HMDB | | Α,β-hydroxypropionate | HMDB | | Α,β-hydroxypropionic acid | HMDB | | R-Glycerate | HMDB | | (R)-Glyceric acid | HMDB | | D-Glycerate | HMDB | | D-Glyceric acid | HMDB | | (2R)-2,3-Dihydroxypropanoic acid | HMDB | | (R)-2,3-Dihydroxypropanoic acid | HMDB | | D-2,3-Dihydroxypropanoic acid | HMDB | | 1-Amino-2-hydroxyethane | HMDB | | 2-Amino-1-ethanol | HMDB | | 2-Amino-ethanol | HMDB | | 2-Aminoethan-1-ol | HMDB | | 2-Aminoethyl alcohol | HMDB | | 2-Hydroxyethylamine | HMDB | | Aethanolamin | HMDB | | Aminoethanol | HMDB | | beta-Aminoethanol | HMDB | | beta-Aminoethyl alcohol | HMDB | | beta-Ethanolamine | HMDB | | beta-Hydroxyethylamine | HMDB | | Colamine | HMDB | | ETA | HMDB | | Glycinol | HMDB | | Hea | HMDB | | MEA | HMDB | | MONOETHANOLAMINE | HMDB | | b-Aminoethanol | HMDB | | Β-aminoethanol | HMDB | | b-Aminoethyl alcohol | HMDB | | Β-aminoethyl alcohol | HMDB | | b-Ethanolamine | HMDB | | Β-ethanolamine | HMDB | | b-Hydroxyethylamine | HMDB | | Β-hydroxyethylamine | HMDB | | 2-Aminoethanol | HMDB | | 2-Ethanolamine | HMDB | | 2-Hydroxyethanamine | HMDB | | Envision conditioner PDD 9020 | HMDB | | Ethylolamine | HMDB | | H-Glycinol | HMDB | | Monoaethanolamin | HMDB | | Olamine | HMDB | | 2 Aminoethanol | HMDB | | (3R,4S,5R)-5-[(1R)-1-Carboxy-2,2-difluoro-1-(phosphonooxy)ethoxy]-4-hydroxy-3-(phosphonooxy)cyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxylate | HMDB | | (1S)-2-[(3-O-b-D-Glucopyranosyl-b-D-galactopyranosyl)oxy]-1-{[(9E)-octadec-9-enoyloxy]methyl}ethyl (10E)-nonadec-10-enoate | HMDB | | (1S)-2-[(3-O-b-D-Glucopyranosyl-b-D-galactopyranosyl)oxy]-1-{[(9E)-octadec-9-enoyloxy]methyl}ethyl (10E)-nonadec-10-enoic acid | HMDB | | (1S)-2-[(3-O-beta-D-Glucopyranosyl-beta-D-galactopyranosyl)oxy]-1-{[(9E)-octadec-9-enoyloxy]methyl}ethyl (10E)-nonadec-10-enoic acid | HMDB | | (1S)-2-[(3-O-Β-D-glucopyranosyl-β-D-galactopyranosyl)oxy]-1-{[(9E)-octadec-9-enoyloxy]methyl}ethyl (10E)-nonadec-10-enoate | HMDB | | (1S)-2-[(3-O-Β-D-glucopyranosyl-β-D-galactopyranosyl)oxy]-1-{[(9E)-octadec-9-enoyloxy]methyl}ethyl (10E)-nonadec-10-enoic acid | HMDB |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C5H9NO4 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 147.1293 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 147.053157781 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | (2S)-2-aminopentanedioic acid |
|---|
| Traditional Name | L-glutamic acid |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 56-86-0 |
|---|
| SMILES | N[C@@H](CCC(O)=O)C(O)=O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C5H9NO4/c6-3(5(9)10)1-2-4(7)8/h3H,1-2,6H2,(H,7,8)(H,9,10)/t3-/m0/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | WHUUTDBJXJRKMK-VKHMYHEASA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as glutamic acid and derivatives. Glutamic acid and derivatives are compounds containing glutamic acid or a derivative thereof resulting from reaction of glutamic acid at the amino group or the carboxy group, or from the replacement of any hydrogen of glycine by a heteroatom. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Class | Carboxylic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Amino acids, peptides, and analogues |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Glutamic acid and derivatives |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Glutamic acid or derivatives
- Alpha-amino acid
- L-alpha-amino acid
- Amino fatty acid
- Dicarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Fatty acid
- Fatty acyl
- Amino acid
- Carboxylic acid
- Organic oxide
- Primary amine
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Primary aliphatic amine
- Organopnictogen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Organic oxygen compound
- Amine
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Aliphatic acyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
| Physiological effect | |
|---|
| Disposition | Biological locationRoute of exposureSourceEndogenousExogenousFood- Food (HMDB: HMDB0000148)
Animal originHerb and spiceVegetableFruitNutCereal and cereal productPulseGourdCoffee and coffee productSoyTeaBaking goodDishAquatic originBeverageBaby foodUnclassified food or beverageFat and oilMilk and milk productOther milk productFermented milk productUnfermented milk- Milk (Other mammals) (FooDB: FOOD00690)
- Milk (Human) (FooDB: FOOD00666)
- Milk (Cow) (FooDB: FOOD00618)
- Cow milk, pasteurized, vitamin A + D added, 0% fat (FooDB: FOOD00889)
- Cow milk, pasteurized, vitamin A + D added, 1% fat (FooDB: FOOD00890)
- Cow milk, pasteurized, vitamin A + D added, 2% fat (FooDB: FOOD00891)
- Cow milk, pasteurized, vitamin D added, 3.25% fat (FooDB: FOOD00892)
Fermented milk Cocoa and cocoa productSnackConfectioneryEgg
|
|---|
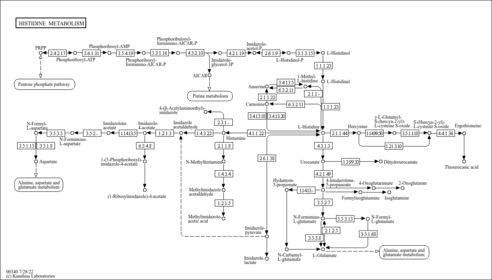
| Process | Naturally occurring processBiological processBiochemical pathwayMetabolic pathwayDisease pathway- Argininosuccinic Aciduria (HMDB: HMDB0000148)
- Cystinosis, Ocular Nonnephropathic (HMDB: HMDB0000148)
- Glutaminolysis and Cancer (PathBank: SMP0108773)
- 2-Methyl-3-hydroxybutryl-CoA Dehydrogenase Deficiency (PathBank: SMP0120439)
- 4-Hydroxybutyric Aciduria/Succinic Semialdehyde Dehydrogenase Deficiency (PathBank: SMP0120445)
- 5-Oxoprolinuria (PathBank: SMP0120446)
- Arginine: Glycine Amidinotransferase Deficiency (AGAT Deficiency) (PathBank: SMP0120454)
- GABA-Transaminase Deficiency (PathBank: SMP0120478)
- Histidinemia (PathBank: SMP0120493)
- Leukotriene C4 Synthesis Deficiency (PathBank: SMP0120510)
- Sarcosinemia (PathBank: SMP0120521)
- Methylenetetrahydrofolate Reductase Deficiency (MTHFRD) (PathBank: SMP0120522)
- Methylmalonate Semialdehyde Dehydrogenase Deficiency (PathBank: SMP0120523)
- Salla Disease/Infantile Sialic Acid Storage Disease (PathBank: SMP0120524)
- Gamma-Glutamyltranspeptidase Deficiency (PathBank: SMP0120566)
- Creatine Deficiency, Guanidinoacetate Methyltransferase Deficiency (PathBank: SMP0120569)
- Xanthinuria Type II (PathBank: SMP0120578)
- Isovaleric Acidemia (PathBank: SMP0120589)
- G(M2)-Gangliosidosis: Variant B, Tay-Sachs Disease (PathBank: SMP0120599)
- Succinic Semialdehyde Dehydrogenase Deficiency (PathBank: SMP0120631)
- Pyridoxine Dependency with Seizures (PathBank: SMP0120635)
- 3-Methylglutaconic Aciduria Type I (PathBank: SMP0120663)
- Argininemia (PathBank: SMP0120676)
- Beta-Ketothiolase Deficiency (PathBank: SMP0120679)
- Canavan Disease (PathBank: SMP0120681)
- Carbamoyl Phosphate Synthetase Deficiency (PathBank: SMP0120682)
- Dihydropyrimidine Dehydrogenase Deficiency (DHPD) (PathBank: SMP0120694)
- Glutaric Aciduria Type I (PathBank: SMP0120704)
- Gout or Kelley-Seegmiller Syndrome (PathBank: SMP0120709)
- Xanthine Dehydrogenase Deficiency (Xanthinuria) (PathBank: SMP0120717)
- Hyperprolinemia Type I (PathBank: SMP0120719)
- Hypoacetylaspartia (PathBank: SMP0120722)
- Tyrosinemia Type 3 (TYRO3) (PathBank: SMP0120731)
- Ornithine Transcarbamylase Deficiency (OTC Deficiency) (PathBank: SMP0120762)
- Tyrosinemia, Transient, of the Newborn (PathBank: SMP0120779)
- Beta-Mercaptolactate-Cysteine Disulfiduria (PathBank: SMP0120783)
- Hyperornithinemia with Gyrate Atrophy (HOGA) (PathBank: SMP0120789)
- 3-Hydroxyisobutyric Aciduria (PathBank: SMP0120806)
- Mitochondrial DNA Depletion Syndrome (PathBank: SMP0120820)
- Non-Ketotic Hyperglycinemia (PathBank: SMP0120534)
- Pyruvate Carboxylase Deficiency (PathBank: SMP0120535)
- Prolinemia Type II (PathBank: SMP0120539)
- Phenylketonuria (PathBank: SMP0120540)
- Prolidase Deficiency (PD) (PathBank: SMP0120541)
- Sialuria or French Type Sialuria (PathBank: SMP0000216)
- The Oncogenic Action of 2-Hydroxyglutarate (PathBank: SMP0002291)
- 3-Methylcrotonyl-CoA Carboxylase Deficiency Type I (PathBank: SMP0120441)
- 3-Methylglutaconic Aciduria Type IV (PathBank: SMP0120444)
- Gamma-Glutamyltransferase Deficiency (PathBank: SMP0120480)
- Hyperprolinemia Type II (PathBank: SMP0120501)
- Tyrosinemia Type 2 (or Richner-Hanhart Syndrome) (PathBank: SMP0120513)
- Methylmalonic Aciduria (PathBank: SMP0120525)
- Primary Hyperoxaluria Type I (PathBank: SMP0120543)
- Tay-Sachs Disease (PathBank: SMP0120545)
- Carnosinuria, Carnosinemia (PathBank: SMP0120558)
- L-Arginine:Glycine Amidinotransferase Deficiency (PathBank: SMP0120572)
- 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA Lyase Deficiency (PathBank: SMP0120661)
- 3-Methylglutaconic Aciduria Type III (PathBank: SMP0120664)
- Adenylosuccinate Lyase Deficiency (PathBank: SMP0120670)
- AICA-Ribosiduria (PathBank: SMP0120673)
- Hawkinsinuria (PathBank: SMP0120711)
- Lactic Acidemia (PathBank: SMP0120724)
- Tyrosinemia Type I (PathBank: SMP0120729)
- Methylmalonic Aciduria Due to Cobalamin-Related Disorders (PathBank: SMP0120748)
- Purine Nucleoside Phosphorylase Deficiency (PathBank: SMP0120756)
- Hyperornithinemia-Hyperammonemia-Homocitrullinuria [HHH-syndrome] (PathBank: SMP0120790)
- Hyperlysinemia I, Familial (PathBank: SMP0120811)
- Hyperlysinemia II or Saccharopinuria (PathBank: SMP0120812)
- Adenine Phosphoribosyltransferase Deficiency (APRT) (PathBank: SMP0120819)
- Myoadenylate Deaminase Deficiency (PathBank: SMP0120821)
- 2-Aminoadipic 2-Oxoadipic Aciduria (PathBank: SMP0120870)
- 3-Phosphoglycerate Dehydrogenase Deficiency (PathBank: SMP0120872)
- Adenosine Deaminase Deficiency (PathBank: SMP0120448)
- Alkaptonuria (PathBank: SMP0120453)
- Citrullinemia Type I (PathBank: SMP0120466)
- Glutathione Synthetase Deficiency (PathBank: SMP0120485)
- Homocarnosinosis (PathBank: SMP0120494)
- Lesch-Nyhan Syndrome (LNS) (PathBank: SMP0120508)
- Maple Syrup Urine Disease (PathBank: SMP0120516)
- Propionic Acidemia (PathBank: SMP0120537)
- Ornithine Aminotransferase Deficiency (OAT Deficiency) (PathBank: SMP0120538)
- Dopamine beta-Hydroxylase Deficiency (PathBank: SMP0120563)
- 5-Oxoprolinase Deficiency (PathBank: SMP0120565)
- Isobutyryl-CoA Dehydrogenase Deficiency (PathBank: SMP0120588)
- 2-Hydroxyglutric Aciduria (D and L Form) (PathBank: SMP0120659)
- Dimethylglycine Dehydrogenase Deficiency (PathBank: SMP0120695)
- Guanidinoacetate Methyltransferase Deficiency (GAMT Deficiency) (PathBank: SMP0120710)
- Isovaleric Aciduria (PathBank: SMP0120723)
- Malonic Aciduria (PathBank: SMP0120734)
- Saccharopinuria/Hyperlysinemia II (PathBank: SMP0120746)
- Molybdenum Cofactor Deficiency (PathBank: SMP0120752)
- Hyperglycinemia, Non-Ketotic (PathBank: SMP0120770)
- Malonyl-CoA Decarboxylase Deficiency (PathBank: SMP0120786)
- Monoamine Oxidase-A Deficiency (MAO-A) (PathBank: SMP0120817)
- Hyperinsulinism-Hyperammonemia Syndrome (PathBank: SMP0120496)
- Xanthinuria Type I (PathBank: SMP0120577)
- 3-Hydroxyisobutyric Acid Dehydrogenase Deficiency (PathBank: SMP0120586)
- Cystinosis, Ocular Nonnephropathic (PathBank: SMP0120654)
- Folate Malabsorption, Hereditary (PathBank: SMP0120656)
- 2-Methyl-3-hydroxybutryl-CoA Dehydrogenase Deficiency (PathBank: SMP0000137)
- Hyperornithinemia-Hyperammonemia-Homocitrullinuria [HHH-syndrome] (PathBank: SMP0000506)
- Mitochondrial DNA Depletion Syndrome (PathBank: SMP0000536)
- The Oncogenic Action of L-2-Hydroxyglutarate in Hydroxygluaricaciduria (PathBank: SMP0002358)
- The Oncogenic Action of D-2-Hydroxyglutarate in Hydroxygluaricaciduria (PathBank: SMP0002359)
Drug action pathwayProtein pathway |
|---|
| Role | |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Molecular Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | 8.57 mg/mL | Not Available | | LogP | -3.69 | HANSCH,C ET AL. (1995) |
|
|---|
| Experimental Chromatographic Properties | Experimental Collision Cross Sections |
|---|
| Predicted Molecular Properties | |
|---|
| Predicted Chromatographic Properties | Predicted Collision Cross SectionsPredicted Retention Times Underivatized| Chromatographic Method | Retention Time | Reference |
|---|
| Measured using a Waters Acquity ultraperformance liquid chromatography (UPLC) ethylene-bridged hybrid (BEH) C18 column (100 mm × 2.1 mm; 1.7 μmparticle diameter). Predicted by Afia on May 17, 2022. Predicted by Afia on May 17, 2022. | 1.0 minutes | 32390414 | | Predicted by Siyang on May 30, 2022 | 9.2343 minutes | 33406817 | | Predicted by Siyang using ReTip algorithm on June 8, 2022 | 7.62 minutes | 32390414 | | AjsUoB = Accucore 150 Amide HILIC with 10mM Ammonium Formate, 0.1% Formic Acid | 400.3 seconds | 40023050 | | Fem_Long = Waters ACQUITY UPLC HSS T3 C18 with Water:MeOH and 0.1% Formic Acid | 484.2 seconds | 40023050 | | Fem_Lipids = Ascentis Express C18 with (60:40 water:ACN):(90:10 IPA:ACN) and 10mM NH4COOH + 0.1% Formic Acid | 318.7 seconds | 40023050 | | Life_Old = Waters ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18 with Water:(20:80 acetone:ACN) and 0.1% Formic Acid | 40.7 seconds | 40023050 | | Life_New = RP Waters ACQUITY UPLC HSS T3 C18 with Water:(30:70 MeOH:ACN) and 0.1% Formic Acid | 195.1 seconds | 40023050 | | RIKEN = Waters ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18 with Water:ACN and 0.1% Formic Acid | 67.9 seconds | 40023050 | | Eawag_XBridgeC18 = XBridge C18 3.5u 2.1x50 mm with Water:MeOH and 0.1% Formic Acid | 287.9 seconds | 40023050 | | BfG_NTS_RP1 =Agilent Zorbax Eclipse Plus C18 (2.1 mm x 150 mm, 3.5 um) with Water:ACN and 0.1% Formic Acid | 220.1 seconds | 40023050 | | HILIC_BDD_2 = Merck SeQuant ZIC-HILIC with ACN(0.1% formic acid):water(16 mM ammonium formate) | 836.1 seconds | 40023050 | | UniToyama_Atlantis = RP Waters Atlantis T3 (2.1 x 150 mm, 5 um) with ACN:Water and 0.1% Formic Acid | 584.5 seconds | 40023050 | | BDD_C18 = Hypersil Gold 1.9µm C18 with Water:ACN and 0.1% Formic Acid | 39.3 seconds | 40023050 | | UFZ_Phenomenex = Kinetex Core-Shell C18 2.6 um, 3.0 x 100 mm, Phenomenex with Water:MeOH and 0.1% Formic Acid | 677.2 seconds | 40023050 | | SNU_RIKEN_POS = Waters ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18 with Water:ACN and 0.1% Formic Acid | 198.7 seconds | 40023050 | | RPMMFDA = Waters ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18 with Water:ACN and 0.1% Formic Acid | 277.0 seconds | 40023050 | | MTBLS87 = Merck SeQuant ZIC-pHILIC column with ACN:Water and :ammonium carbonate | 725.9 seconds | 40023050 | | KI_GIAR_zic_HILIC_pH2_7 = Merck SeQuant ZIC-HILIC with ACN:Water and 0.1% FA | 480.3 seconds | 40023050 | | Meister zic-pHILIC pH9.3 = Merck SeQuant ZIC-pHILIC column with ACN:Water 5mM NH4Ac pH9.3 and 5mM ammonium acetate in water | 478.6 seconds | 40023050 |
Predicted Kovats Retention IndicesUnderivatizedDerivatized| Derivative Name / Structure | SMILES | Kovats RI Value | Column Type | Reference |
|---|
| L-Glutamic acid,1TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O | 1507.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Glutamic acid,1TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CCC(=O)O | 1472.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Glutamic acid,1TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCC(=O)O)C(=O)O | 1533.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Glutamic acid,2TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1518.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Glutamic acid,2TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 1617.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Glutamic acid,2TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCC(=O)O)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1589.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Glutamic acid,2TMS,isomer #4 | C[Si](C)(C)N([C@@H](CCC(=O)O)C(=O)O)[Si](C)(C)C | 1729.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Glutamic acid,3TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1625.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Glutamic acid,3TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1664.7 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Glutamic acid,3TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1807.9 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | L-Glutamic acid,3TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)CC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 1779.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Glutamic acid,3TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)CC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 1718.7 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Glutamic acid,3TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)CC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 1969.6 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | L-Glutamic acid,3TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@H](CCC(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 1765.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Glutamic acid,3TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@H](CCC(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 1708.5 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Glutamic acid,3TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@H](CCC(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 1949.2 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | L-Glutamic acid,4TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)CC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 1804.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Glutamic acid,4TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)CC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 1776.6 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Glutamic acid,4TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)CC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 1746.4 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | L-Glutamic acid,1TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O | 1765.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Glutamic acid,1TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CCC(=O)O | 1743.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Glutamic acid,1TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCC(=O)O)C(=O)O | 1797.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Glutamic acid,2TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 1982.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Glutamic acid,2TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 2094.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Glutamic acid,2TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCC(=O)O)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2043.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Glutamic acid,2TBDMS,isomer #4 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N([C@@H](CCC(=O)O)C(=O)O)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2168.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Glutamic acid,3TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2272.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Glutamic acid,3TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2259.4 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Glutamic acid,3TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2195.4 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | L-Glutamic acid,3TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)CC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2433.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Glutamic acid,3TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)CC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2321.6 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Glutamic acid,3TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)CC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2263.8 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | L-Glutamic acid,3TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@H](CCC(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2427.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Glutamic acid,3TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@H](CCC(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2289.5 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Glutamic acid,3TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@H](CCC(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2256.1 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | L-Glutamic acid,4TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)CC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2668.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Glutamic acid,4TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)CC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2533.6 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Glutamic acid,4TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)CC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2243.6 | Standard polar | 33892256 |
|
|---|
| GC-MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Glutamic acid GC-EI-TOF (Pegasus III TOF-MS system, Leco; GC 6890, Agilent Technologies) (3 TMS) | splash10-0002-2950000000-2d6edc93ec5f8dee2223 | 2014-06-16 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Glutamic acid GC-EI-TOF (Pegasus III TOF-MS system, Leco; GC 6890, Agilent Technologies) (Non-derivatized) | splash10-002b-0940000000-4e285988bc537825d94d | 2014-06-16 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Glutamic acid GC-EI-TOF (Pegasus III TOF-MS system, Leco; GC 6890, Agilent Technologies) (3 TMS) | splash10-00dj-9630000000-1ecc76aab86283892139 | 2014-06-16 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Glutamic acid GC-MS (2 TMS) | splash10-001i-8910000000-00f65ced0c55aa4ad169 | 2014-06-16 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Glutamic acid GC-MS (3 TMS) | splash10-0032-3980000000-3069de5b6c49e4176968 | 2014-06-16 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Glutamic acid EI-B (Non-derivatized) | splash10-0002-0790000000-79d3e289c22cb183faa1 | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Glutamic acid GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-0002-2950000000-2d6edc93ec5f8dee2223 | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Glutamic acid GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-002b-0940000000-4e285988bc537825d94d | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Glutamic acid GC-EI-QQ (Non-derivatized) | splash10-00ea-6932100000-30d3f5dcc198a5971e96 | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Glutamic acid GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-00dj-9630000000-1ecc76aab86283892139 | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Glutamic acid GC-MS (Non-derivatized) | splash10-001i-8910000000-00f65ced0c55aa4ad169 | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Glutamic acid GC-MS (Non-derivatized) | splash10-0032-3980000000-3069de5b6c49e4176968 | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Glutamic acid GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-0znc-9300000000-f88e86b78a4cee99a2d4 | 2016-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Glutamic acid GC-MS (2 TMS) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-00di-8290000000-f99e03763f636e557887 | 2017-10-06 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Glutamic acid GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Glutamic acid GC-MS (TMS_1_1) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Glutamic acid GC-MS (TMS_1_2) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Glutamic acid GC-MS (TMS_1_3) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Glutamic acid GC-MS (TMS_2_2) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Glutamic acid GC-MS (TMS_2_3) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Glutamic acid GC-MS (TMS_2_4) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Glutamic acid GC-MS (TBDMS_1_1) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Glutamic acid GC-MS (TBDMS_1_2) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Glutamic acid GC-MS (TBDMS_1_3) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Glutamic acid GC-MS (TBDMS_2_1) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
MS/MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glutamic acid Quattro_QQQ 10V, Positive-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-003r-6900000000-95b0a084dc076f9c7b91 | 2012-07-24 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glutamic acid Quattro_QQQ 25V, Positive-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-001i-9000000000-c37d4c80a14ec029ef63 | 2012-07-24 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glutamic acid Quattro_QQQ 40V, Positive-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-0a59-9000000000-6f1888aa71bcb0adf76c | 2012-07-24 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glutamic acid LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Positive-QTOF | splash10-004j-0900000000-5fa8a338dcd2f2a6bdd2 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glutamic acid LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Positive-QTOF | splash10-004i-0900000000-16763200aa07f7629ad4 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glutamic acid LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Positive-QTOF | splash10-03di-3900000000-d9cfc5187aa799f6f978 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glutamic acid LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Positive-QTOF | splash10-0a4i-0900000000-10ee9a593e13550bec1c | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glutamic acid LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Positive-QTOF | splash10-0002-0900000000-4d045a3c1fc6e56f801b | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glutamic acid LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Positive-QTOF | splash10-001i-9000000000-c3c7f8f3754109a0c25b | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glutamic acid LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Positive-QTOF | splash10-004i-0900000000-48bfae26c69408b7f0ae | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glutamic acid LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Positive-QTOF | splash10-0002-0900000000-82c2a681e7522a7bb1d1 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glutamic acid LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Negative-QTOF | splash10-0002-0905010000-af1c9ec4d0062fa6960e | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glutamic acid LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Negative-QTOF | splash10-01q9-9700000000-2b967b896a6e48914512 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glutamic acid LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Negative-QTOF | splash10-004i-0900000000-1434321646181ea894a0 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glutamic acid LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Negative-QTOF | splash10-00di-0900000000-11fadb2530828eedad8a | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glutamic acid LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Negative-QTOF | splash10-006t-0941100000-07d051890cb1d9e5c856 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glutamic acid LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Negative-QTOF | splash10-004i-9200000000-f8619d11f1f54d836bb1 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glutamic acid LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Negative-QTOF | splash10-004i-0900000000-ea2dd00e79ef06e8dc04 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glutamic acid LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Negative-QTOF | splash10-00di-0900000000-3e239d4014c95a2ef873 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glutamic acid LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0002-0900000000-b548959edce39d319cf4 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glutamic acid LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0udi-0900000000-40d901f655797db2cd0f | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glutamic acid LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 30V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0udi-1900000000-f997527a39900ac431c7 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glutamic acid LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0udi-7900000000-60816f0601a4e6d25ffb | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glutamic acid LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 50V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0007-9000000000-6ee821f657c604d1afca | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Glutamic acid LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-000t-0900000000-7c02624abe56da9247a2 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum |
NMR Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Experimental 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, H2O, experimental) | 2021-10-10 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Experimental 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, H2O, experimental) | 2021-10-10 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Experimental 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, H2O, experimental) | 2021-10-10 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Experimental 2D NMR | [1H, 13C]-HSQC NMR Spectrum (2D, 600 MHz, H2O, experimental) | 2012-12-04 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
IR Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted IR Spectrum | IR Ion Spectrum (Predicted IRIS Spectrum, Adduct: [M-H]-) | 2023-02-03 | FELIX lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted IR Spectrum | IR Ion Spectrum (Predicted IRIS Spectrum, Adduct: [M+H]+) | 2023-02-03 | FELIX lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted IR Spectrum | IR Ion Spectrum (Predicted IRIS Spectrum, Adduct: [M+Na]+) | 2023-02-03 | FELIX lab | View Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Disease References | | Epilepsy |
|---|
- Rainesalo S, Keranen T, Palmio J, Peltola J, Oja SS, Saransaari P: Plasma and cerebrospinal fluid amino acids in epileptic patients. Neurochem Res. 2004 Jan;29(1):319-24. [PubMed:14992292 ]
| | Schizophrenia |
|---|
- Alfredsson G, Wiesel FA: Monoamine metabolites and amino acids in serum from schizophrenic patients before and during sulpiride treatment. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 1989;99(3):322-7. [PubMed:2480613 ]
- Do KQ, Lauer CJ, Schreiber W, Zollinger M, Gutteck-Amsler U, Cuenod M, Holsboer F: gamma-Glutamylglutamine and taurine concentrations are decreased in the cerebrospinal fluid of drug-naive patients with schizophrenic disorders. J Neurochem. 1995 Dec;65(6):2652-62. [PubMed:7595563 ]
- Fukushima T, Iizuka H, Yokota A, Suzuki T, Ohno C, Kono Y, Nishikiori M, Seki A, Ichiba H, Watanabe Y, Hongo S, Utsunomiya M, Nakatani M, Sadamoto K, Yoshio T: Quantitative analyses of schizophrenia-associated metabolites in serum: serum D-lactate levels are negatively correlated with gamma-glutamylcysteine in medicated schizophrenia patients. PLoS One. 2014 Jul 8;9(7):e101652. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0101652. eCollection 2014. [PubMed:25004141 ]
- Koike S, Bundo M, Iwamoto K, Suga M, Kuwabara H, Ohashi Y, Shinoda K, Takano Y, Iwashiro N, Satomura Y, Nagai T, Natsubori T, Tada M, Yamasue H, Kasai K: A snapshot of plasma metabolites in first-episode schizophrenia: a capillary electrophoresis time-of-flight mass spectrometry study. Transl Psychiatry. 2014 Apr 8;4:e379. doi: 10.1038/tp.2014.19. [PubMed:24713860 ]
- Yang J, Chen T, Sun L, Zhao Z, Qi X, Zhou K, Cao Y, Wang X, Qiu Y, Su M, Zhao A, Wang P, Yang P, Wu J, Feng G, He L, Jia W, Wan C: Potential metabolite markers of schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry. 2013 Jan;18(1):67-78. doi: 10.1038/mp.2011.131. Epub 2011 Oct 25. [PubMed:22024767 ]
| | Alzheimer's disease |
|---|
- Fonteh AN, Harrington RJ, Tsai A, Liao P, Harrington MG: Free amino acid and dipeptide changes in the body fluids from Alzheimer's disease subjects. Amino Acids. 2007 Feb;32(2):213-24. Epub 2006 Oct 10. [PubMed:17031479 ]
| | Heart failure |
|---|
- Norrelund H, Wiggers H, Halbirk M, Frystyk J, Flyvbjerg A, Botker HE, Schmitz O, Jorgensen JO, Christiansen JS, Moller N: Abnormalities of whole body protein turnover, muscle metabolism and levels of metabolic hormones in patients with chronic heart failure. J Intern Med. 2006 Jul;260(1):11-21. [PubMed:16789974 ]
| | Lipoyltransferase 1 Deficiency |
|---|
- Soreze Y, Boutron A, Habarou F, Barnerias C, Nonnenmacher L, Delpech H, Mamoune A, Chretien D, Hubert L, Bole-Feysot C, Nitschke P, Correia I, Sardet C, Boddaert N, Hamel Y, Delahodde A, Ottolenghi C, de Lonlay P: Mutations in human lipoyltransferase gene LIPT1 cause a Leigh disease with secondary deficiency for pyruvate and alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2013 Dec 17;8:192. doi: 10.1186/1750-1172-8-192. [PubMed:24341803 ]
| | Dicarboxylic aminoaciduria |
|---|
- Melancon SB, Dallaire L, Lemieux B, Robitaille P, Potier M: Dicarboxylic aminoaciduria: an inborn error of amino acid conservation. J Pediatr. 1977 Sep;91(3):422-7. [PubMed:894411 ]
| | N-acetylglutamate synthetase deficiency |
|---|
- Guffon N, Vianey-Saban C, Bourgeois J, Rabier D, Colombo JP, Guibaud P: A new neonatal case of N-acetylglutamate synthase deficiency treated by carbamylglutamate. J Inherit Metab Dis. 1995;18(1):61-5. [PubMed:7623444 ]
| | Stomach cancer |
|---|
- Yu L, Aa J, Xu J, Sun M, Qian S, Cheng L, Yang S, Shi R: Metabolomic phenotype of gastric cancer and precancerous stages based on gas chromatography time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011 Aug;26(8):1290-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2011.06724.x. [PubMed:21443661 ]
| | Anoxia |
|---|
- Zupke C, Sinskey AJ, Stephanopoulos G: Intracellular flux analysis applied to the effect of dissolved oxygen on hybridomas. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 1995 Dec;44(1-2):27-36. [PubMed:8579834 ]
| | Leukemia |
|---|
- Peng CT, Wu KH, Lan SJ, Tsai JJ, Tsai FJ, Tsai CH: Amino acid concentrations in cerebrospinal fluid in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia undergoing chemotherapy. Eur J Cancer. 2005 May;41(8):1158-63. Epub 2005 Apr 14. [PubMed:15911239 ]
| | Rett syndrome |
|---|
- Lappalainen R, Riikonen RS: High levels of cerebrospinal fluid glutamate in Rett syndrome. Pediatr Neurol. 1996 Oct;15(3):213-6. [PubMed:8916158 ]
| | Sepsis |
|---|
- Stewart CJ, Embleton ND, Marrs ECL, Smith DP, Fofanova T, Nelson A, Skeath T, Perry JD, Petrosino JF, Berrington JE, Cummings SP: Longitudinal development of the gut microbiome and metabolome in preterm neonates with late onset sepsis and healthy controls. Microbiome. 2017 Jul 12;5(1):75. doi: 10.1186/s40168-017-0295-1. [PubMed:28701177 ]
| | Diverticular disease |
|---|
- Tursi A, Mastromarino P, Capobianco D, Elisei W, Miccheli A, Capuani G, Tomassini A, Campagna G, Picchio M, Giorgetti G, Fabiocchi F, Brandimarte G: Assessment of Fecal Microbiota and Fecal Metabolome in Symptomatic Uncomplicated Diverticular Disease of the Colon. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2016 Oct;50 Suppl 1:S9-S12. doi: 10.1097/MCG.0000000000000626. [PubMed:27622378 ]
| | Obesity |
|---|
- Haro C, Montes-Borrego M, Rangel-Zuniga OA, Alcala-Diaz JF, Gomez-Delgado F, Perez-Martinez P, Delgado-Lista J, Quintana-Navarro GM, Tinahones FJ, Landa BB, Lopez-Miranda J, Camargo A, Perez-Jimenez F: Two Healthy Diets Modulate Gut Microbial Community Improving Insulin Sensitivity in a Human Obese Population. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016 Jan;101(1):233-42. doi: 10.1210/jc.2015-3351. Epub 2015 Oct 27. [PubMed:26505825 ]
| | Ulcerative colitis |
|---|
- Bjerrum JT, Wang Y, Hao F, Coskun M, Ludwig C, Gunther U, Nielsen OH: Metabonomics of human fecal extracts characterize ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease and healthy individuals. Metabolomics. 2015;11:122-133. Epub 2014 Jun 1. [PubMed:25598765 ]
- Kolho KL, Pessia A, Jaakkola T, de Vos WM, Velagapudi V: Faecal and Serum Metabolomics in Paediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J Crohns Colitis. 2017 Mar 1;11(3):321-334. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjw158. [PubMed:27609529 ]
- Azario I, Pievani A, Del Priore F, Antolini L, Santi L, Corsi A, Cardinale L, Sawamoto K, Kubaski F, Gentner B, Bernardo ME, Valsecchi MG, Riminucci M, Tomatsu S, Aiuti A, Biondi A, Serafini M: Neonatal umbilical cord blood transplantation halts skeletal disease progression in the murine model of MPS-I. Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 25;7(1):9473. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-09958-9. [PubMed:28842642 ]
| | Crohn's disease |
|---|
- Bjerrum JT, Wang Y, Hao F, Coskun M, Ludwig C, Gunther U, Nielsen OH: Metabonomics of human fecal extracts characterize ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease and healthy individuals. Metabolomics. 2015;11:122-133. Epub 2014 Jun 1. [PubMed:25598765 ]
- Kolho KL, Pessia A, Jaakkola T, de Vos WM, Velagapudi V: Faecal and Serum Metabolomics in Paediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J Crohns Colitis. 2017 Mar 1;11(3):321-334. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjw158. [PubMed:27609529 ]
- Azario I, Pievani A, Del Priore F, Antolini L, Santi L, Corsi A, Cardinale L, Sawamoto K, Kubaski F, Gentner B, Bernardo ME, Valsecchi MG, Riminucci M, Tomatsu S, Aiuti A, Biondi A, Serafini M: Neonatal umbilical cord blood transplantation halts skeletal disease progression in the murine model of MPS-I. Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 25;7(1):9473. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-09958-9. [PubMed:28842642 ]
| | Autism |
|---|
- De Angelis M, Piccolo M, Vannini L, Siragusa S, De Giacomo A, Serrazzanetti DI, Cristofori F, Guerzoni ME, Gobbetti M, Francavilla R: Fecal microbiota and metabolome of children with autism and pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified. PLoS One. 2013 Oct 9;8(10):e76993. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076993. eCollection 2013. [PubMed:24130822 ]
| | Colorectal cancer |
|---|
- Weir TL, Manter DK, Sheflin AM, Barnett BA, Heuberger AL, Ryan EP: Stool microbiome and metabolome differences between colorectal cancer patients and healthy adults. PLoS One. 2013 Aug 6;8(8):e70803. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0070803. Print 2013. [PubMed:23940645 ]
- Ni Y, Xie G, Jia W: Metabonomics of human colorectal cancer: new approaches for early diagnosis and biomarker discovery. J Proteome Res. 2014 Sep 5;13(9):3857-70. doi: 10.1021/pr500443c. Epub 2014 Aug 14. [PubMed:25105552 ]
- Sinha R, Ahn J, Sampson JN, Shi J, Yu G, Xiong X, Hayes RB, Goedert JJ: Fecal Microbiota, Fecal Metabolome, and Colorectal Cancer Interrelations. PLoS One. 2016 Mar 25;11(3):e0152126. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0152126. eCollection 2016. [PubMed:27015276 ]
- Lin Y, Ma C, Liu C, Wang Z, Yang J, Liu X, Shen Z, Wu R: NMR-based fecal metabolomics fingerprinting as predictors of earlier diagnosis in patients with colorectal cancer. Oncotarget. 2016 May 17;7(20):29454-64. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8762. [PubMed:27107423 ]
- Brown DG, Rao S, Weir TL, O'Malia J, Bazan M, Brown RJ, Ryan EP: Metabolomics and metabolic pathway networks from human colorectal cancers, adjacent mucosa, and stool. Cancer Metab. 2016 Jun 6;4:11. doi: 10.1186/s40170-016-0151-y. eCollection 2016. [PubMed:27275383 ]
- Wang X, Wang J, Rao B, Deng L: Gut flora profiling and fecal metabolite composition of colorectal cancer patients and healthy individuals. Exp Ther Med. 2017 Jun;13(6):2848-2854. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.4367. Epub 2017 Apr 20. [PubMed:28587349 ]
| | Irritable bowel syndrome |
|---|
- Ponnusamy K, Choi JN, Kim J, Lee SY, Lee CH: Microbial community and metabolomic comparison of irritable bowel syndrome faeces. J Med Microbiol. 2011 Jun;60(Pt 6):817-27. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.028126-0. Epub 2011 Feb 17. [PubMed:21330412 ]
| | Periodontal disease |
|---|
- Sugimoto M, Wong DT, Hirayama A, Soga T, Tomita M: Capillary electrophoresis mass spectrometry-based saliva metabolomics identified oral, breast and pancreatic cancer-specific profiles. Metabolomics. 2010 Mar;6(1):78-95. Epub 2009 Sep 10. [PubMed:20300169 ]
| | Pancreatic cancer |
|---|
- Sugimoto M, Wong DT, Hirayama A, Soga T, Tomita M: Capillary electrophoresis mass spectrometry-based saliva metabolomics identified oral, breast and pancreatic cancer-specific profiles. Metabolomics. 2010 Mar;6(1):78-95. Epub 2009 Sep 10. [PubMed:20300169 ]
- Xie G, Lu L, Qiu Y, Ni Q, Zhang W, Gao YT, Risch HA, Yu H, Jia W: Plasma metabolite biomarkers for the detection of pancreatic cancer. J Proteome Res. 2015 Feb 6;14(2):1195-202. doi: 10.1021/pr501135f. Epub 2014 Dec 8. [PubMed:25429707 ]
| | Perillyl alcohol administration for cancer treatment |
|---|
- Sugimoto M, Wong DT, Hirayama A, Soga T, Tomita M: Capillary electrophoresis mass spectrometry-based saliva metabolomics identified oral, breast and pancreatic cancer-specific profiles. Metabolomics. 2010 Mar;6(1):78-95. Epub 2009 Sep 10. [PubMed:20300169 ]
| | Eosinophilic esophagitis |
|---|
- Slae, M., Huynh, H., Wishart, D.S. (2014). Analysis of 30 normal pediatric urine samples via NMR spectroscopy (unpublished work). NA.
| | Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease |
|---|
- Gronwald W, Klein MS, Zeltner R, Schulze BD, Reinhold SW, Deutschmann M, Immervoll AK, Boger CA, Banas B, Eckardt KU, Oefner PJ: Detection of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease by NMR spectroscopic fingerprinting of urine. Kidney Int. 2011 Jun;79(11):1244-53. doi: 10.1038/ki.2011.30. Epub 2011 Mar 9. [PubMed:21389975 ]
|
|
|---|
| General References | - Molinari F, Raas-Rothschild A, Rio M, Fiermonte G, Encha-Razavi F, Palmieri L, Palmieri F, Ben-Neriah Z, Kadhom N, Vekemans M, Attie-Bitach T, Munnich A, Rustin P, Colleaux L: Impaired mitochondrial glutamate transport in autosomal recessive neonatal myoclonic epilepsy. Am J Hum Genet. 2005 Feb;76(2):334-9. Epub 2004 Dec 8. [PubMed:15592994 ]
- Sreekumar A, Poisson LM, Rajendiran TM, Khan AP, Cao Q, Yu J, Laxman B, Mehra R, Lonigro RJ, Li Y, Nyati MK, Ahsan A, Kalyana-Sundaram S, Han B, Cao X, Byun J, Omenn GS, Ghosh D, Pennathur S, Alexander DC, Berger A, Shuster JR, Wei JT, Varambally S, Beecher C, Chinnaiyan AM: Metabolomic profiles delineate potential role for sarcosine in prostate cancer progression. Nature. 2009 Feb 12;457(7231):910-4. doi: 10.1038/nature07762. [PubMed:19212411 ]
- Silwood CJ, Lynch E, Claxson AW, Grootveld MC: 1H and (13)C NMR spectroscopic analysis of human saliva. J Dent Res. 2002 Jun;81(6):422-7. [PubMed:12097436 ]
- Zupke C, Sinskey AJ, Stephanopoulos G: Intracellular flux analysis applied to the effect of dissolved oxygen on hybridomas. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 1995 Dec;44(1-2):27-36. [PubMed:8579834 ]
- Nicholson JK, O'Flynn MP, Sadler PJ, Macleod AF, Juul SM, Sonksen PH: Proton-nuclear-magnetic-resonance studies of serum, plasma and urine from fasting normal and diabetic subjects. Biochem J. 1984 Jan 15;217(2):365-75. [PubMed:6696735 ]
- Peng CT, Wu KH, Lan SJ, Tsai JJ, Tsai FJ, Tsai CH: Amino acid concentrations in cerebrospinal fluid in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia undergoing chemotherapy. Eur J Cancer. 2005 May;41(8):1158-63. Epub 2005 Apr 14. [PubMed:15911239 ]
- Cynober LA: Plasma amino acid levels with a note on membrane transport: characteristics, regulation, and metabolic significance. Nutrition. 2002 Sep;18(9):761-6. [PubMed:12297216 ]
- Rainesalo S, Keranen T, Palmio J, Peltola J, Oja SS, Saransaari P: Plasma and cerebrospinal fluid amino acids in epileptic patients. Neurochem Res. 2004 Jan;29(1):319-24. [PubMed:14992292 ]
- Mross K, Maessen P, van der Vijgh WJ, Gall H, Boven E, Pinedo HM: Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of epidoxorubicin and doxorubicin in humans. J Clin Oncol. 1988 Mar;6(3):517-26. [PubMed:3162516 ]
- Noorlander CW, de Graan PN, Nikkels PG, Schrama LH, Visser GH: Distribution of glutamate transporters in the human placenta. Placenta. 2004 Jul;25(6):489-95. [PubMed:15135231 ]
- Grasselli G, Vigano L, Capri G, Locatelli A, Tarenzi E, Spreafico C, Bertuzzi A, Giani A, Materazzo C, Cresta S, Perotti A, Valagussa P, Gianni L: Clinical and pharmacologic study of the epirubicin and paclitaxel combination in women with metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2001 Apr 15;19(8):2222-31. [PubMed:11304775 ]
- Frayn KN, Khan K, Coppack SW, Elia M: Amino acid metabolism in human subcutaneous adipose tissue in vivo. Clin Sci (Lond). 1991 May;80(5):471-4. [PubMed:1851687 ]
- Alfredsson G, Wiesel FA, Tylec A: Relationships between glutamate and monoamine metabolites in cerebrospinal fluid and serum in healthy volunteers. Biol Psychiatry. 1988 Apr 1;23(7):689-97. [PubMed:2453224 ]
- Zoia C, Cogliati T, Tagliabue E, Cavaletti G, Sala G, Galimberti G, Rivolta I, Rossi V, Frattola L, Ferrarese C: Glutamate transporters in platelets: EAAT1 decrease in aging and in Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging. 2004 Feb;25(2):149-57. [PubMed:14749132 ]
- Rizzo V, Anesi A, Montalbetti L, Bellantoni G, Trotti R, Melzi d'Eril GV: Reference values of neuroactive amino acids in the cerebrospinal fluid by high-performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical and fluorescence detection. J Chromatogr A. 1996 Apr 5;729(1-2):181-8. [PubMed:9004939 ]
- Agnati LF, Ferre S, Lluis C, Franco R, Fuxe K: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutical implications of intramembrane receptor/receptor interactions among heptahelical receptors with examples from the striatopallidal GABA neurons. Pharmacol Rev. 2003 Sep;55(3):509-50. Epub 2003 Jul 17. [PubMed:12869660 ]
- Rutten EP, Engelen MP, Wouters EF, Schols AM, Deutz NE: Metabolic effects of glutamine and glutamate ingestion in healthy subjects and in persons with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Clin Nutr. 2006 Jan;83(1):115-23. [PubMed:16400059 ]
- Agarwal A, Tripathi LM, Pandey VC: Status of ammonia, glutamate, lactate and pyruvate during Plasmodium yoelii infection and pyrimethamine treatment in mice. J Commun Dis. 1997 Sep;29(3):235-41. [PubMed:9465528 ]
- Heuschen UA, Allemeyer EH, Hinz U, Langer K, Heuschen G, Decker-Baumann C, Herfarth C, Stern J: Glutamine distribution in patients with ulcerative colitis and in patients with familial adenomatous polyposis coli before and after restorative proctocolectomy. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2002 Jul;17(4):245-52. Epub 2001 Dec 18. [PubMed:12073073 ]
- Olson RC: A proposed role for nerve growth factor in the etiology of multiple sclerosis. Med Hypotheses. 1998 Dec;51(6):493-8. [PubMed:10052870 ]
- Nakamura K, Matsumura K, Kobayashi S, Kaneko T: Sympathetic premotor neurons mediating thermoregulatory functions. Neurosci Res. 2005 Jan;51(1):1-8. [PubMed:15596234 ]
- Corrie JE, DeSantis A, Katayama Y, Khodakhah K, Messenger JB, Ogden DC, Trentham DR: Postsynaptic activation at the squid giant synapse by photolytic release of L-glutamate from a 'caged' L-glutamate. J Physiol. 1993 Jun;465:1-8. [PubMed:7901400 ]
- Reeds PJ, Burrin DG, Stoll B, Jahoor F: Intestinal glutamate metabolism. J Nutr. 2000 Apr;130(4S Suppl):978S-82S. [PubMed:10736365 ]
- Smith QR: Transport of glutamate and other amino acids at the blood-brain barrier. J Nutr. 2000 Apr;130(4S Suppl):1016S-22S. [PubMed:10736373 ]
- Okumoto S, Looger LL, Micheva KD, Reimer RJ, Smith SJ, Frommer WB: Detection of glutamate release from neurons by genetically encoded surface-displayed FRET nanosensors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Jun 14;102(24):8740-5. Epub 2005 Jun 6. [PubMed:15939876 ]
- Augustin H, Grosjean Y, Chen K, Sheng Q, Featherstone DE: Nonvesicular release of glutamate by glial xCT transporters suppresses glutamate receptor clustering in vivo. J Neurosci. 2007 Jan 3;27(1):111-23. [PubMed:17202478 ]
- Elshenawy S, Pinney SE, Stuart T, Doulias PT, Zura G, Parry S, Elovitz MA, Bennett MJ, Bansal A, Strauss JF 3rd, Ischiropoulos H, Simmons RA: The Metabolomic Signature of the Placenta in Spontaneous Preterm Birth. Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 4;21(3). pii: ijms21031043. doi: 10.3390/ijms21031043. [PubMed:32033212 ]
|
|---|