| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 5.0 |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Quantified |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2006-05-22 15:12:30 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2022-03-07 02:49:17 UTC |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0003073 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | |
|---|
| Metabolite Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | gamma-Linolenic acid |
|---|
| Description | gamma-Linolenic acid, also known as 18:3n6 or GLA, belongs to the class of organic compounds known as linoleic acids and derivatives. These are derivatives of linoleic acid. Linoleic acid is a polyunsaturated omega-6 18-carbon long fatty acid, with two CC double bonds at the 9- and 12-positions. gamma-Linolenic acid is a very hydrophobic molecule, practically insoluble (in water), and relatively neutral. gamma-Linolenic acid is an omega-6 fatty acid produced in the body as the delta 6-desaturase metabolite of linoleic acid. It is converted into dihomo-gamma-linolenic acid, a biosynthetic precursor of monoenoic prostaglandins such as PGE1 (PubChem). |
|---|
| Structure | CCCCC\C=C/C\C=C/C\C=C/CCCCC(O)=O InChI=1S/C18H30O2/c1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15-16-17-18(19)20/h6-7,9-10,12-13H,2-5,8,11,14-17H2,1H3,(H,19,20)/b7-6-,10-9-,13-12- |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| (6,9,12)-Linolenic acid | ChEBI | | (6Z,9Z,12Z)-Octadecatrienoic acid | ChEBI | | (Z,Z,Z)-6,9,12-Octadecatrienoic acid | ChEBI | | 18:3 (N-6) | ChEBI | | 6,9,12-Octadecatrienoic acid | ChEBI | | 6-cis,9-cis,12-cis-Octadecatrienoic acid | ChEBI | | all-cis-6,9,12-Octadecatrienoic acid | ChEBI | | C18:3 (N-6) | ChEBI | | C18:3, N-6,9,12 all-cis | ChEBI | | cis-Delta(6,9,12)-Octadecatrienoic acid | ChEBI | | gamma-Linolensaeure | ChEBI | | Gamoleic acid | ChEBI | | Gamolenic acid | ChEBI | | GLA | ChEBI | | Octadeca-6,9,12-triensaeure | ChEBI | | (6,9,12)-Linolenate | Generator | | (6Z,9Z,12Z)-Octadecatrienoate | Generator | | (Z,Z,Z)-6,9,12-Octadecatrienoate | Generator | | 6,9,12-Octadecatrienoate | Generator | | 6-cis,9-cis,12-cis-Octadecatrienoate | Generator | | all-cis-6,9,12-Octadecatrienoate | Generator | | cis-delta(6,9,12)-Octadecatrienoate | Generator | | cis-Δ(6,9,12)-octadecatrienoate | Generator | | cis-Δ(6,9,12)-octadecatrienoic acid | Generator | | g-Linolensaeure | Generator | | Γ-linolensaeure | Generator | | Gamoleate | Generator | | Gamolenate | Generator | | g-Linolenate | Generator | | g-Linolenic acid | Generator | | gamma-Linolenate | Generator | | Γ-linolenate | Generator | | Γ-linolenic acid | Generator | | 6(Z),9(Z),12(Z)-Octadecatrienoate | HMDB | | 6(Z),9(Z),12(Z)-Octadecatrienoic acid | HMDB | | 6,9,12-all-cis-Octadecatrienoate | HMDB | | 6,9,12-all-cis-Octadecatrienoic acid | HMDB | | 6Z,9Z,12Z-Octadecatrienoate | HMDB | | 6Z,9Z,12Z-Octadecatrienoic acid | HMDB | | gamma-Llnolenic acid | HMDB | | Ligla | HMDB | | Acid, gamma-linolenic | HMDB | | Acid, gamolenic | HMDB | | gamma Linolenic acid | HMDB | | FA(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) | HMDB | | FA(18:3n6) | HMDB | | Linolenate | HMDB | | gamma-Linolenic acid | KEGG | | (6Z,9Z,12Z)-6,9,12-Octadecatrienoic acid | PhytoBank | | (Z,Z,Z)-6,9,12-Octatrienoic acid | PhytoBank | | cis,cis,cis-6,9,12-Octadecatrienoic acid | PhytoBank | | cis-6,cis-9,cis-12-Octadecatrienoic acid | PhytoBank |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C18H30O2 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 278.4296 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 278.224580204 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | (6Z,9Z,12Z)-octadeca-6,9,12-trienoic acid |
|---|
| Traditional Name | gamma linolenic acid |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 506-26-3 |
|---|
| SMILES | CCCCC\C=C/C\C=C/C\C=C/CCCCC(O)=O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C18H30O2/c1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15-16-17-18(19)20/h6-7,9-10,12-13H,2-5,8,11,14-17H2,1H3,(H,19,20)/b7-6-,10-9-,13-12- |
|---|
| InChI Key | VZCCETWTMQHEPK-QNEBEIHSSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as lineolic acids and derivatives. These are derivatives of lineolic acid. Lineolic acid is a polyunsaturated omega-6 18 carbon long fatty acid, with two CC double bonds at the 9- and 12-positions. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules |
|---|
| Class | Fatty Acyls |
|---|
| Sub Class | Lineolic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Lineolic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Octadecanoid
- Long-chain fatty acid
- Fatty acid
- Unsaturated fatty acid
- Straight chain fatty acid
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Carboxylic acid
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organic oxide
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organooxygen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Aliphatic acyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
| Physiological effect | Not Available |
|---|
| Disposition | |
|---|
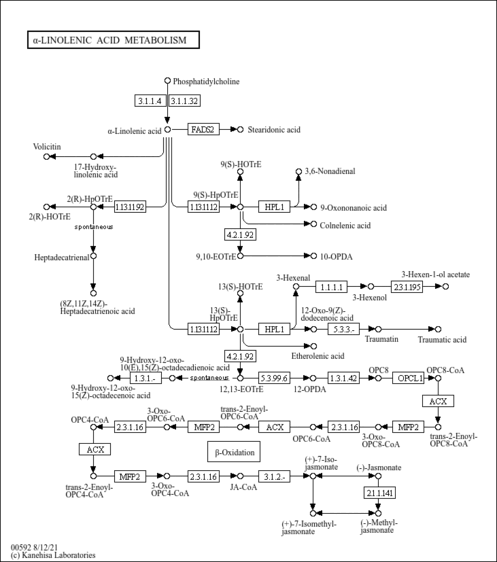
| Process | Naturally occurring processBiological processBiochemical pathwayMetabolic pathway- Alpha Linolenic Acid and Linoleic Acid Metabolism (PathBank: SMP0087171)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(16:0/16:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012473)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(16:0/18:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012485)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(16:0/18:1(9Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012497)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(16:0/18:1(11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012509)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(16:0/18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012521)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(16:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0012528)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(16:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0012529)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(16:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012530)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(16:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012531)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(16:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012532)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(16:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012533)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(16:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012534)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(16:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0012535)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(16:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012536)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(16:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012537)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(16:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0012538)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(16:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012539)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(16:0/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012545)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(16:0/20:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012557)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(16:0/20:1(11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012569)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(16:0/20:1(13Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012581)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(16:0/22:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012593)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(16:0/22:1(13Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012605)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:0/16:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012617)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:0/18:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012629)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:0/18:1(9Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012641)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:0/18:1(11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012653)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:0/18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012665)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0012672)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0012673)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012674)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012675)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012676)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012677)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012678)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0012679)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012680)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012681)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0012682)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012683)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:0/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012689)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:0/20:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012701)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:0/20:1(11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012713)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:0/20:1(13Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012725)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:0/22:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012737)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:0/22:1(13Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012749)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:1(9Z)/16:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012761)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:1(9Z)/18:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012773)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012785)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:1(9Z)/18:1(11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012797)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:1(9Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012809)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:1(9Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0012816)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:1(9Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0012817)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:1(9Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012818)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:1(9Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012819)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:1(9Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012820)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:1(9Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012821)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:1(9Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012822)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:1(9Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0012823)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:1(9Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012824)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:1(9Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012825)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:1(9Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0012826)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:1(9Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012827)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:1(9Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012833)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:1(9Z)/20:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012845)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:1(9Z)/20:1(11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012857)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:1(9Z)/20:1(13Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012869)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:1(9Z)/22:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012881)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:1(9Z)/22:1(13Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012893)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:1(11Z)/16:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012905)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:1(11Z)/18:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012917)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:1(11Z)/18:1(9Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012929)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:1(11Z)/18:1(11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012941)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:1(11Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012953)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:1(11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0012960)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:1(11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0012961)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:1(11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012962)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:1(11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012963)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:1(11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012964)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:1(11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012965)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:1(11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012966)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:1(11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0012967)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:1(11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012968)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:1(11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012969)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:1(11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0012970)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:1(11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012971)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:1(11Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012977)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:1(11Z)/20:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0012989)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:1(11Z)/20:1(11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013001)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:1(11Z)/20:1(13Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013013)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:1(11Z)/22:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013025)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:1(11Z)/22:1(13Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013037)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:2(9Z,12Z)/16:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013049)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013061)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:1(9Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013073)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:1(11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013085)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013097)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0013104)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0013105)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013106)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013107)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013108)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013109)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013110)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0013111)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013112)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013113)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0013114)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013115)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013121)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:2(9Z,12Z)/20:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013133)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:2(9Z,12Z)/20:1(11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013145)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:2(9Z,12Z)/20:1(13Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013157)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:2(9Z,12Z)/22:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013169)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:2(9Z,12Z)/22:1(13Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013181)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/16:0/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0013188)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/16:0/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0013189)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/16:0/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013190)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/16:0/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013191)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/16:0/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013192)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/16:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013193)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/16:0/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013194)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/16:0/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0013195)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/16:0/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013196)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/16:0/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013197)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/16:0/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0013198)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/16:0/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013199)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:0/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0013200)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:0/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0013201)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:0/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013202)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:0/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013203)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:0/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013204)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013205)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:0/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013206)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:0/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0013207)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:0/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013208)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:0/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013209)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:0/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0013210)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:0/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013211)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:1(9Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0013212)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:1(9Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0013213)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013214)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:1(9Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013215)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:1(9Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013216)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:1(9Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013217)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:1(9Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013218)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:1(9Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0013219)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:1(9Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013220)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:1(9Z)/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013221)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:1(9Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0013222)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:1(9Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013223)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:1(11Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0013224)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:1(11Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0013225)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:1(11Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013226)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:1(11Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013227)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:1(11Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013228)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:1(11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013229)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:1(11Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013230)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:1(11Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0013231)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:1(11Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013232)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:1(11Z)/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013233)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:1(11Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0013234)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:1(11Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013235)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0013236)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0013237)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013238)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013239)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013240)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013241)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0013533)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013242)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0013243)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013244)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013245)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0013246)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013247)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0013248)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0013249)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013250)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013251)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013252)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013253)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013254)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0013255)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013256)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013257)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0013258)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013259)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0013260)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0013261)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013262)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013263)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013264)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013265)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013266)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0013267)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013268)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013269)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0013270)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013271)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:0/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0013272)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:0/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0013273)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:0/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013274)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:0/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013275)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:0/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013276)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013277)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:0/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013278)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:0/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0013279)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:0/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013280)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:0/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013281)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:0/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0013282)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:0/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013283)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:1(11Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0013284)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:1(11Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0013285)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:1(11Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013286)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:1(11Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013287)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:1(11Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013288)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:1(11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013289)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:1(11Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013290)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:1(11Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0013291)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:1(11Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013292)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:1(11Z)/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013293)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:1(11Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0013294)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:1(11Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013295)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:1(13Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0013296)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:1(13Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0013297)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:1(13Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013298)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:1(13Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013299)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:1(13Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013300)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:1(13Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013301)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:1(13Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013302)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:1(13Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0013303)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:1(13Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013304)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:1(13Z)/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013305)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:1(13Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0013306)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:1(13Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013307)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:0/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0013308)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:0/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0013309)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:0/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013310)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:0/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013311)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:0/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013312)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013313)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:0/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013314)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:0/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0013315)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:0/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013316)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:0/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013317)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:0/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0013318)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:0/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013319)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:1(13Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0013320)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:1(13Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0013321)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:1(13Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013322)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:1(13Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013323)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:1(13Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013324)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:1(13Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013325)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:1(13Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013326)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:1(13Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0013327)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:1(13Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013328)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:1(13Z)/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013329)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:1(13Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0013330)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:1(13Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013331)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/16:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013337)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013349)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:1(9Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013361)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:1(11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013372)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013383)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0013389)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0013390)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013391)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013392)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013393)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013394)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013395)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0013396)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013397)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013398)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0013399)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013400)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013406)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013418)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:1(11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013430)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:1(13Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013442)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/22:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013454)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/22:1(13Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013466)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:0/16:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013478)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:0/18:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013490)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:0/18:1(9Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013502)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:0/18:1(11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013514)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:0/18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013526)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0013534)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013535)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013536)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013537)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013538)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013539)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0013540)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013541)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013542)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0013543)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013544)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:0/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013550)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:0/20:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013562)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:0/20:1(11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013574)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:0/20:1(13Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013586)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:0/22:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013598)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:0/22:1(13Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013610)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:1(11Z)/16:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013622)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:1(11Z)/18:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013634)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:1(11Z)/18:1(9Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013646)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:1(11Z)/18:1(11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013658)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:1(11Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013670)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:1(11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0013677)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:1(11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0013678)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:1(11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013679)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:1(11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013680)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:1(11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013681)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:1(11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013682)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:1(11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013683)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:1(11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0013684)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:1(11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013685)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:1(11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013686)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:1(11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0013687)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:1(11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013688)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:1(11Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013694)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:1(11Z)/20:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013706)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:1(11Z)/20:1(11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013718)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:1(11Z)/20:1(13Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013730)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:1(11Z)/22:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013742)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:1(11Z)/22:1(13Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013754)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:1(13Z)/16:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013767)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:1(13Z)/18:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013779)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:1(13Z)/18:1(9Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013791)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:1(13Z)/18:1(11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013803)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:1(13Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013815)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:1(13Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0013822)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:1(13Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0013823)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:1(13Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013824)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:1(13Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013825)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:1(13Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013826)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:1(13Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013827)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:1(13Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013828)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:1(13Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0013829)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:1(13Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013830)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:1(13Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013831)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:1(13Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0013832)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:1(13Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013833)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:1(13Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013839)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:1(13Z)/20:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013851)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:1(13Z)/20:1(11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013863)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:1(13Z)/20:1(13Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013875)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:1(13Z)/22:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013887)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(20:1(13Z)/22:1(13Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013900)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(22:0/16:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013912)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(22:0/18:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013924)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(22:0/18:1(9Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013936)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(22:0/18:1(11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013948)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(22:0/18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013960)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(22:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0013967)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(22:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0013968)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(22:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013969)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(22:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013970)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(22:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013971)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(22:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013972)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(22:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013973)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(22:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0013974)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(22:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013975)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(22:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013976)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(22:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0013977)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(22:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013978)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(22:0/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013984)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(22:0/20:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0013996)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(22:0/20:1(11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014008)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(22:0/20:1(13Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014022)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(22:0/22:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014034)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(22:0/22:1(13Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014046)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(22:1(13Z)/16:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014058)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(22:1(13Z)/18:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014070)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(22:1(13Z)/18:1(9Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014082)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(22:1(13Z)/18:1(11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014094)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(22:1(13Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014106)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(22:1(13Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014113)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(22:1(13Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014114)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(22:1(13Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014115)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(22:1(13Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014116)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(22:1(13Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014117)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(22:1(13Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014118)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(22:1(13Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014119)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(22:1(13Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0014120)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(22:1(13Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014121)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(22:1(13Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014122)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(22:1(13Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0014123)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(22:1(13Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014124)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(22:1(13Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014130)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(22:1(13Z)/20:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014142)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(22:1(13Z)/20:1(11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014154)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(22:1(13Z)/20:1(13Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014167)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(22:1(13Z)/22:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014179)
- Triacylglycerol Degradation TG(22:1(13Z)/22:1(13Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014191)
|
|---|
| Role | |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Liquid |
|---|
| Experimental Molecular Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | Not Available | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Experimental Chromatographic Properties | Experimental Collision Cross Sections |
|---|
| Predicted Molecular Properties | |
|---|
| Predicted Chromatographic Properties | Predicted Collision Cross SectionsPredicted Retention Times Underivatized| Chromatographic Method | Retention Time | Reference |
|---|
| Measured using a Waters Acquity ultraperformance liquid chromatography (UPLC) ethylene-bridged hybrid (BEH) C18 column (100 mm × 2.1 mm; 1.7 μmparticle diameter). Predicted by Afia on May 17, 2022. Predicted by Afia on May 17, 2022. | 8.66 minutes | 32390414 | | Predicted by Siyang on May 30, 2022 | 24.5972 minutes | 33406817 | | Predicted by Siyang using ReTip algorithm on June 8, 2022 | 1.68 minutes | 32390414 | | AjsUoB = Accucore 150 Amide HILIC with 10mM Ammonium Formate, 0.1% Formic Acid | 35.1 seconds | 40023050 | | Fem_Long = Waters ACQUITY UPLC HSS T3 C18 with Water:MeOH and 0.1% Formic Acid | 3035.4 seconds | 40023050 | | Fem_Lipids = Ascentis Express C18 with (60:40 water:ACN):(90:10 IPA:ACN) and 10mM NH4COOH + 0.1% Formic Acid | 627.7 seconds | 40023050 | | Life_Old = Waters ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18 with Water:(20:80 acetone:ACN) and 0.1% Formic Acid | 254.2 seconds | 40023050 | | Life_New = RP Waters ACQUITY UPLC HSS T3 C18 with Water:(30:70 MeOH:ACN) and 0.1% Formic Acid | 452.5 seconds | 40023050 | | RIKEN = Waters ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18 with Water:ACN and 0.1% Formic Acid | 675.6 seconds | 40023050 | | Eawag_XBridgeC18 = XBridge C18 3.5u 2.1x50 mm with Water:MeOH and 0.1% Formic Acid | 1137.9 seconds | 40023050 | | BfG_NTS_RP1 =Agilent Zorbax Eclipse Plus C18 (2.1 mm x 150 mm, 3.5 um) with Water:ACN and 0.1% Formic Acid | 700.5 seconds | 40023050 | | HILIC_BDD_2 = Merck SeQuant ZIC-HILIC with ACN(0.1% formic acid):water(16 mM ammonium formate) | 92.3 seconds | 40023050 | | UniToyama_Atlantis = RP Waters Atlantis T3 (2.1 x 150 mm, 5 um) with ACN:Water and 0.1% Formic Acid | 2263.9 seconds | 40023050 | | BDD_C18 = Hypersil Gold 1.9µm C18 with Water:ACN and 0.1% Formic Acid | 744.7 seconds | 40023050 | | UFZ_Phenomenex = Kinetex Core-Shell C18 2.6 um, 3.0 x 100 mm, Phenomenex with Water:MeOH and 0.1% Formic Acid | 1897.1 seconds | 40023050 | | SNU_RIKEN_POS = Waters ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18 with Water:ACN and 0.1% Formic Acid | 850.5 seconds | 40023050 | | RPMMFDA = Waters ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18 with Water:ACN and 0.1% Formic Acid | 530.6 seconds | 40023050 | | MTBLS87 = Merck SeQuant ZIC-pHILIC column with ACN:Water and :ammonium carbonate | 552.8 seconds | 40023050 | | KI_GIAR_zic_HILIC_pH2_7 = Merck SeQuant ZIC-HILIC with ACN:Water and 0.1% FA | 613.2 seconds | 40023050 | | Meister zic-pHILIC pH9.3 = Merck SeQuant ZIC-pHILIC column with ACN:Water 5mM NH4Ac pH9.3 and 5mM ammonium acetate in water | 8.5 seconds | 40023050 |
Predicted Kovats Retention IndicesUnderivatizedDerivatized |
|---|
| GC-MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - gamma-Linolenic acid GC-MS (1 TMS) | splash10-005c-9800000000-7b6e7a36b048f5ed69bd | 2014-06-16 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - gamma-Linolenic acid GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-00b9-9300000000-254ecb989081fdc719d2 | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - gamma-Linolenic acid GC-MS (Non-derivatized) | splash10-005c-9800000000-7b6e7a36b048f5ed69bd | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - gamma-Linolenic acid GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-0006-9650000000-eec5566c0f0f90bf0049 | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - gamma-Linolenic acid GC-MS (1 TMS) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-007c-9431000000-b239852c91e567668780 | 2017-10-06 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - gamma-Linolenic acid GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - gamma-Linolenic acid GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | MS | Mass Spectrum (Electron Ionization) | splash10-00nf-9200000000-cf911df79059a750cb2a | 2015-03-01 | Not Available | View Spectrum |
MS/MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - gamma-Linolenic acid ESI-TOF 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-005l-0902100000-6fc8730bd28daa779b66 | 2017-08-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - gamma-Linolenic acid ESI-TOF 30V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-005l-0902100000-6fc8730bd28daa779b66 | 2017-08-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - gamma-Linolenic acid ESI-TOF 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-005l-0902100000-6fc8730bd28daa779b66 | 2017-08-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - gamma-Linolenic acid ESI-TOF , Negative-QTOF | splash10-005l-0902100000-6fc8730bd28daa779b66 | 2017-08-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - gamma-Linolenic acid ESI-TOF 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-004i-0090000000-143e6ddfa05656a4c4da | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - gamma-Linolenic acid ESI-TOF 30V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-004i-0090000000-0b9ba563ad074fe141e8 | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - gamma-Linolenic acid ESI-TOF 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-004i-0090000000-63bf7d731625d5577978 | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - gamma-Linolenic acid ESI-TOF 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-004i-0090000000-fbc4e202a8b26c91dc9e | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - gamma-Linolenic acid ESI-TOF , Negative-QTOF | splash10-004i-0090000000-b56d00321ab0921fe7b7 | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - gamma-Linolenic acid LC-ESI-QTOF , negative-QTOF | splash10-004i-0090000000-dcae4273443fd52bbb03 | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - gamma-Linolenic acid LC-ESI-TOF , negative-QTOF | splash10-004i-0090000000-143e6ddfa05656a4c4da | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - gamma-Linolenic acid LC-ESI-TOF , negative-QTOF | splash10-004i-0090000000-0b9ba563ad074fe141e8 | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - gamma-Linolenic acid LC-ESI-TOF , negative-QTOF | splash10-004i-0090000000-63bf7d731625d5577978 | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - gamma-Linolenic acid LC-ESI-QTOF 10V, positive-QTOF | splash10-004i-0090000000-370b301c8afc435a0ce1 | 2020-07-21 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - gamma-Linolenic acid LC-ESI-QTOF 20V, positive-QTOF | splash10-003s-9850000000-54163d6f895368b9032c | 2020-07-21 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - gamma-Linolenic acid LC-ESI-QTOF 40V, positive-QTOF | splash10-001i-9000000000-e6cdb81ac5675944be82 | 2020-07-21 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - gamma-Linolenic acid 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-003s-9750000000-d1947011d4fc6a28a135 | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - gamma-Linolenic acid 30V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-004i-0090000000-0b9ba563ad074fe141e8 | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - gamma-Linolenic acid 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-004i-0090000000-370b301c8afc435a0ce1 | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - gamma-Linolenic acid 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-01t9-0190000000-6b136607b48b31667801 | 2016-08-03 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - gamma-Linolenic acid 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-01q9-4790000000-5046458d5d3e3c228518 | 2016-08-03 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - gamma-Linolenic acid 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-05mo-8930000000-852d50a19eb0b0df729b | 2016-08-03 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - gamma-Linolenic acid 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-004i-0090000000-ab643cae783eb66bf131 | 2016-08-04 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - gamma-Linolenic acid 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0059-1090000000-abce276de392be9d7d3f | 2016-08-04 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - gamma-Linolenic acid 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0a4i-9230000000-40a41feed498373e54d2 | 2016-08-04 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
NMR Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
|
|---|